Orthognathic Surgery
Orthognathic surgery is a unique treatment in maxillofacial surgery that significantly improves the patient’s appearance and occlusal function, resulting in not only aesthetic enhancements but also notable impacts on functional, psychological, and social aspects of the patient’s life.
This surgery compensates for and treats a wide range of problems and conditions related to the jaws, face, head, and neck, both in soft and hard tissues, including injuries and deformities.
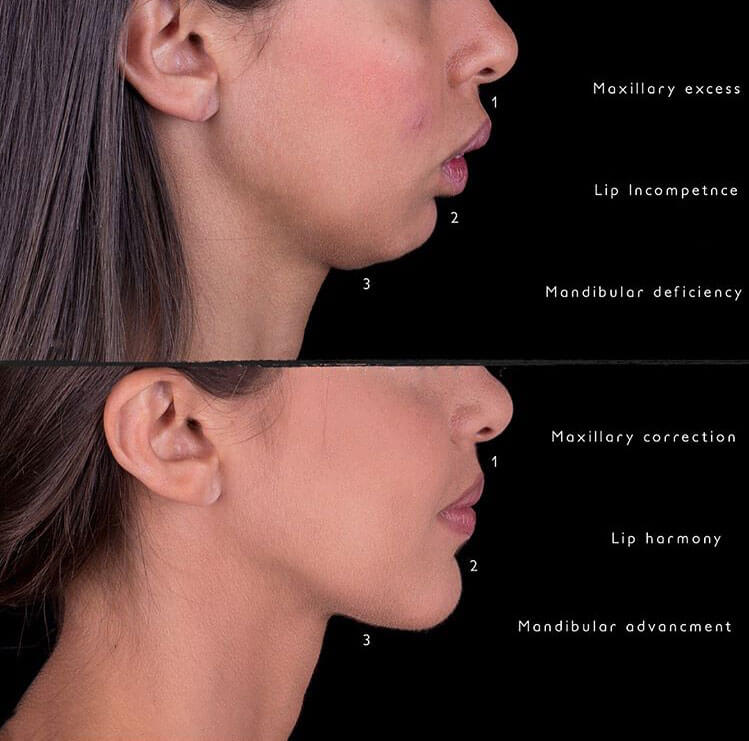
What is Orthognathic Surgery?
Orthognathic Surgery
Successful outcomes in modern orthognathic surgery rely on close collaboration between a maxillofacial surgeon and an orthodontist throughout all stages of treatment, including preoperative planning, duration of orthodontic treatment, jaw surgery, and postoperative orthodontics, and surgical check-ups.
Orthodontic treatment is used to correct the position of the teeth and orthognathic surgery is utilized to correct the position of both the maxilla and mandible bones.
[read more]
The maxillofacial surgeon evaluates the patient’s facial and jaw conditions for achieving functional (occlusal) and aesthetic facial goals. Orthognathic surgery is necessary for patients whose jaw growth is completed but who have minor or major functional or aesthetic defects. This surgery is performed by changing the position of the upper jaw, lower jaw, or chin.
Sometimes patients seek treatment due to dental irregularities and misalignment, and they tend to correct misalignments, height discrepancies, tooth protrusion, or retrusion.
However, after the visit, we realize that the problem is not only dental irregularities but also incorrect relationships between the two jaws and the conditions and position of the chin, which involve skeletal or bone and muscle issues affecting the jaw. As a result of these problems, the patient also experiences dental misalignments and irregularities.
This is where an orthodontist cannot solely resolve the patient’s issue through orthodontic treatment because orthodontics is the science of correcting and treating dental irregularities. To address skeletal and facial problems, a maxillofacial surgeon must perform surgical treatment in conjunction with orthodontics to create the foundation and position of both jaws for orthodontic treatment and correction of dental misalignments.
In modern orthognathic surgery, apart from repositioning the jaws and establishing a desired occlusal relationship, auxiliary techniques are employed, if necessary, to enhance the size or shape of the face (cheeks, chin, nose, and lips). These methods also address any deficiencies in the hard and soft tissues. These auxiliary methods include osseous genioplasty versus alloplasty, rhinoplasty, chin prosthesis, lip prosthesis, cheek prosthesis, or injections in the head, face, and neck area, septorhinoplasty, and neck liposuction, etc.
[/read]
How is the process of orthognathic surgery treatment carried out?
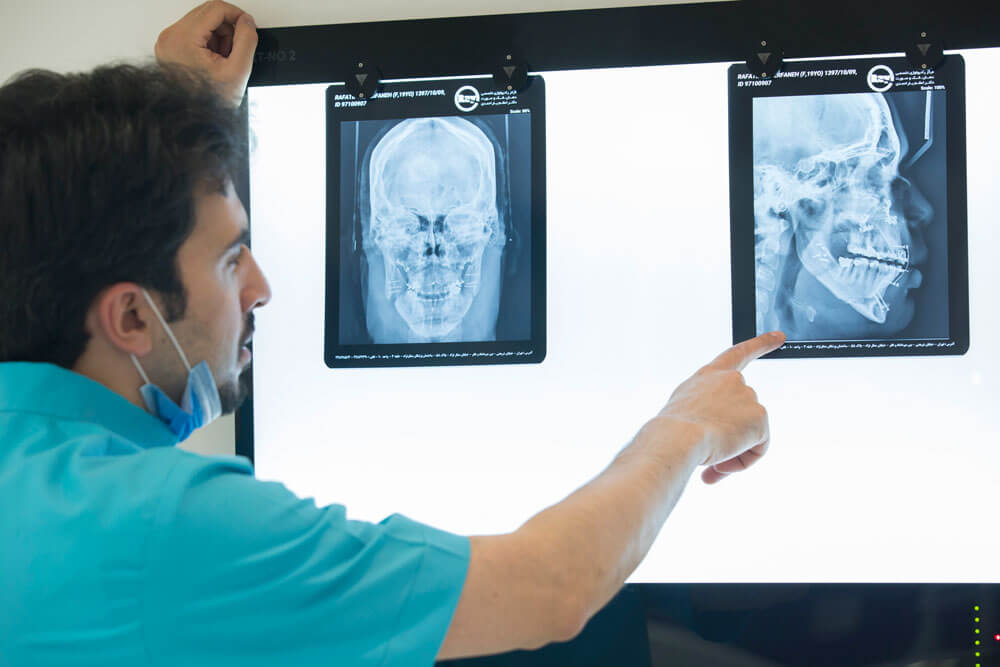
To initiate the treatment, it is essential to establish a precise and collaborative treatment plan between the maxillofacial surgeon and orthodontic specialist. Radiographic images, photographs, and three-dimensional CT scans, as well as dental models provide the physician with a more accurate analysis of the facial and jaw abnormalities and the conditions of the teeth within the jawbone, enabling precise preoperative planning by the surgeon and orthodontist.
[read more]
Following that, the treatment typically begins with an orthodontic specialist. The primary objective of preoperative orthodontics is to align the position of the teeth on the bone. This may involve creating the appropriate inclination, adjusting the transverse arch space, or maintaining dental midline, and orthodontic treatment usually takes around one year to prepare for the surgical procedure. After approximately one to one and a half years, the patient is referred to the specialized maxillofacial department to commence the orthognathic surgical treatment.
Orthognathic surgery may be required for one or both jaws, depending on the patient’s problem and the physician’s treatment plan. The duration of jaw surgery varies between approximately three to four hours, depending on the type of surgery. Safeguarding the teeth, bones, and neural structures is of utmost importance in lower jaw surgical techniques.
Preservation of lingual nerves, subapical alveolar, osteotomy, and protection of soft tissues during the surgical approach are crucial.
Typically, this surgery is performed intraorally, meaning that the position and conditions of the jaws are corrected through intraoral incisions. Depending on the type of operation, the bones may be opened, repositioned, fixated with screws and plates, and bone or soft tissue grafts may be performed if necessary, followed by intraoral sutures.
After the procedure, both jaws are connected to stabilize the achieved position, which is accomplished by securing specialized wires and brackets onto the teeth. The wires are removed approximately two weeks after the surgery, and around one month after the surgery, the patient is referred back to the orthodontic specialist for continued orthodontic treatment to align and position the teeth within the jawbone. The orthodontic treatment continues for approximately one to one and a half years, and upon completion of orthodontics, the patient will have a harmonious and proper facial and jaw position, along with straight and aligned teeth.
Generally, orthosurgery or orthognathic surgery yields remarkable and ideal results for the patient, with noticeable and significant changes. It provides the patient with self-confidence and unique aesthetics. In some cases, jaw or bone-related issues are so severe that they jeopardize the patient’s function, swallowing, speech, and overall health. In this category, after orthognathic surgery, the patient experiences not only remarkable and ideal aesthetics but also functional improvement and better health.
[/read]
Psychological Readiness of Patients
Psychological factors must be thoroughly examined and evaluated by the maxillofacial surgeon and orthodontist. It is essential for the treatment team to understand the patient’s main motivation for treatment and the specific problems they are experiencing. Treatment aims to correct dental deformities and misalignments, skeletal abnormalities of the jaw, forward or backward positioning of the lower jaw, facial symmetry, chin or cheek size modification, changes in facial profile, the distance between the lips and nose, and functional issues as well as the psychological and social impact on the patient’s quality of life need to be analyzed to assess the patient’s psychological response and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
[read more]
Patient expectations and their alignment with the proposed treatment plan by the orthodontist are directly related. However, sometimes patients may not be inclined towards an orthognathic treatment plan due to its lengthy duration and associated costs. In such cases, it should be understood that orthodontic treatment without correcting the jaw relationships and occlusion is not feasible for patients with skeletal jaw problems.
Patient counseling regarding the treatment process, costs, jaw surgery procedures, surgical complications, advantages and disadvantages, recovery period, orthodontic duration, etc., are as important as the treatment techniques themselves. Patients should be informed about dietary changes, speech techniques, eating principles, work principles, and post-operative instructions so that they can adjust their lifestyle accordingly during the initial 4 to 6 weeks after the surgery.
During the post-operative days, some patients may experience discomfort and distress due to complete and prolonged rest, which is a short-term phase, and everything returns to normal with the improvement of the surgical area. Psychological readiness for orthognathic surgery is vital, and the patient must feel the necessity for surgery and corrections to be more determined than before to undergo the treatment.
Depending on the type of procedure, most patients can return to work or university approximately two weeks later. Pain and swelling are usually controlled during the first two weeks, but instructions and care should still be followed for up to one month.
[/read]
Orthognathic Jaw Surgery
If you are concerned about a protruding or receding jaw and are seeking cosmetic treatments or jaw surgery, you can contact Dr. Alireza Modaresi, a maxillofacial surgeon, for a consultation and to develop a treatment plan.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
- Saturdays: 14:00 to 20:00 - Punak clinic
- Sundays: 14:00 to 20:00 - Shariati clinic
- Mondays: 14:00 to 20:00 - Punak clinic
- Thursday: 14:00 to 20:00 - Saveh clinic
Abnormalities of Jaw and Facial Skeleton
Types of Abnormalities:
- Class 1 Skeletal Abnormality
- Class 2 Skeletal Abnormality
- Class 2 problems are divided into two other categories: Class II Divisions
- Class 3 Skeletal Abnormality
- Mandibular Deviation
This form of jaw is considered to have a correct and normal jaw relationship, where the skeletal position is in the correct position relative to the entire face, and the dental relationship is also aligned, with the lower front teeth located behind the upper front teeth.
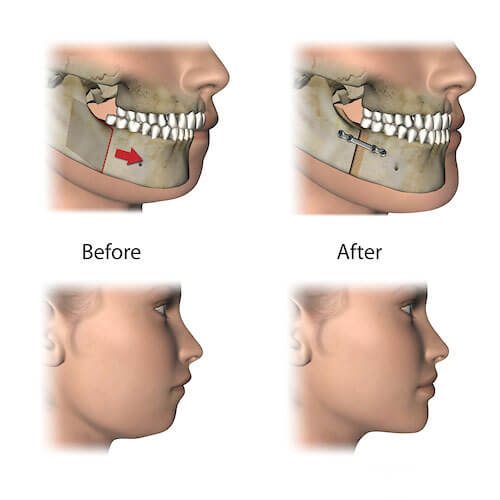
In this abnormality, the lower jaw is positioned further back and the upper jaw is positioned further forward. In these cases, the jaw angles are not well defined, and the patient exhibits a prominent double chin. Other signs in this category of patients include having a gummy smile or showing a large portion of the teeth and gums while smiling.
- In cases where the patient has a gummy smile, the height of the upper jaw is excessive. By reducing the height of the upper jaw, removing excess bone and stabilizing it in the desired location, the visibility of the gums during smiling can be reduced.
- In the correction procedure for this upper jaw abnormality, the upper jaw is moved backward and upward, and the lower jaw is moved forward. It should be noted that after the procedure, assessing the position of the chin can also raise the possibility of genioplasty in addition to lower jaw surgery.
Class II Division 1: In this condition, there is excessive overjet and a noticeable discrepancy between the two jaws.
Class II Division 2: The upper front teeth are positioned towards the back, causing dental irregularity or deep bite. In this case, dental irregularity is more noticeable than the jaw abnormality.
In these individuals, the lower jaw is positioned forward and the upper jaw is positioned backward, usually accompanied by bilateral collapse of the nasal sidewalls. Another sign of this abnormality is a more prominent mandible. In the treatment of these patients, the upper jaw is moved forward and the lower jaw is moved backward, placing both jaws in their proper positions and correcting the facial shape.
This condition occurs when the lower jaw deviates to one side. A visible sign of this abnormality is that the midline or centerline of the teeth has shifted to the other side. This condition can occur genetically or as a result of trauma and incorrect healing of a jaw fracture, causing improper fusion of the jawbone.
- Asymmetries
- Open Bite
- Vertical Maxillary Deficiency
This is a condition where the jaw is tilted due to excessive growth on one side of the jaw, resulting in the asymmetry between the two sides of the jaw.
In some patients, temporomandibular joint grows more on one side due to unknown reasons, resulting in jaw deviation, which is called hemimandibular hypertrophy.
This condition has its roots in childhood and is common among individuals who had a habit of sucking on pacifiers or their own fingers during their childhood. In this abnormality, while the back teeth are in contact with each other, the front teeth of the upper and lower jaws do not meet. In these patients, the anterior open bite is treated by correcting the horizontal angle of the upper jaw. This procedure is performed surgically through a procedure called BiMax surgery.
This is a condition in which patients have a lack of height in the front teeth of the face. This means that the gums and teeth are not visible at all when smiling.
In some patients, temporomandibular joint grows excessively on one side due to unknown reasons, resulting in jaw deviation, which is referred to as hemimandibular hypertrophy.
Upper Jaw Surgery
Types of Abnormalities:
When the upper jaw protrudes significantly or moves backward, it can lead to the following underlying bone problems:
Open Bite: When the back teeth (molars) do not touch when your mouth is closed.
Crossbite: When some of your lower teeth are positioned outside of your upper teeth when your mouth is closed.
Hyperplasia: Refers to the forward and downward position of the upper jaw.
Hypoplasia: Refers to the backward and upward position of the upper jaw.
Insufficient bone width in the upper jaw (or narrow bone width and excessive palate depth): this abnormality is treated with procedures such as SARPE (Surgically Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion).
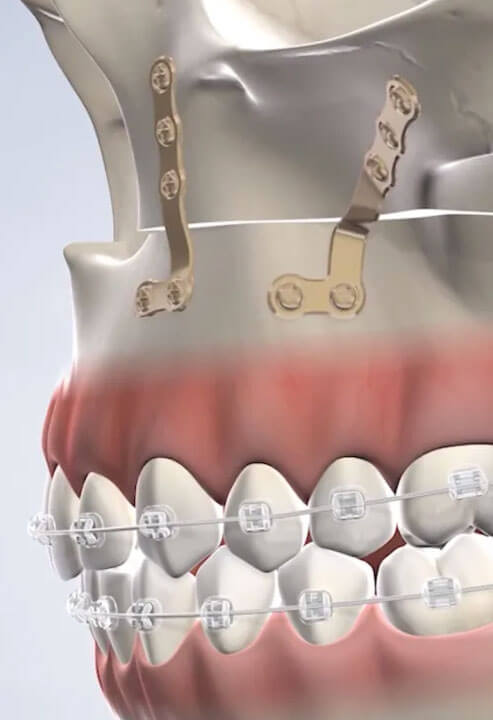
Upper Jaw Surgery Techniques
Le Fort 1: In this surgery, a full-thickness bone incision is made, and the bone is moved forward, backward, and upward.
High Le Fort: In this type of surgery, the upper jaw incision is slightly higher, compensating for the recessed tissue around the nose.
Upper Jaw Osteotomy: This surgery is performed on the upper jaw to correct open bite or crossbite. During this procedure, the upper jaw and teeth are moved forward to align with the lower jaw and teeth.
Segmental Osteotomy: It refers to dividing the upper jaw into two or three sections in order to achieve optimal positioning of the upper jaw.
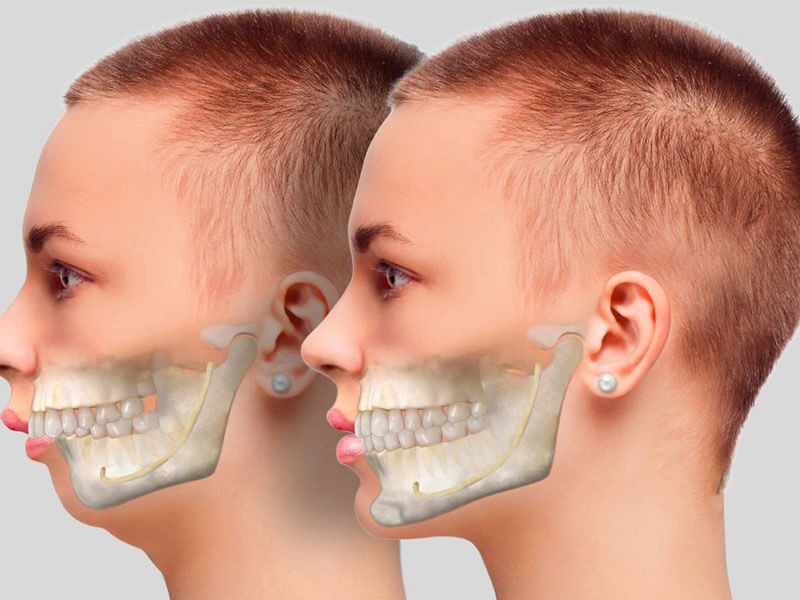
Mandibular Surgery (Lower Jaw)
Types of Abnormalities:
Lower jaw abnormalities are often characterized by anterior or posterior positioning of the lower jaw, and the maxillofacial surgeon aims to correct aesthetic or skeletal defects using the following methods.
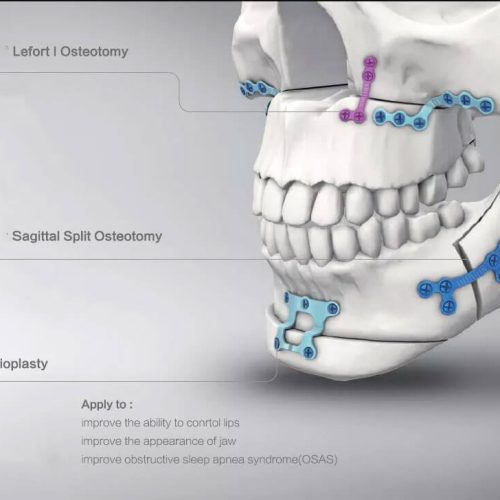
Lower Jaw Surgery Techniques
Lower Jaw Osteotomy: It is often performed when your lower jaw protrudes or is set back significantly. The jaw bone is incised by the jaw surgeon using two methods: SSRO (Sagittal Split Ramus Osteotomy) or IVRO (Intraoral Vertical Ramus Osteotomy).
The jaw is separated, and after placing it back in its original and proper position, bone fixation is done with specialized titanium plates and screws. This surgery corrects issues such as overbite and protrusion of the lower jaw. The surgeon makes an incision at the back of your mouth to move the lower jaw forward or backward.
IVRO or Subcondylar: For this surgery, the surgeon makes an incision through the entire thickness of the mandibular bone at the posterior aspect, the ramus bone is cut, and it is repositioned in its new and proper position.
SSRO: During this surgery, the bone is split in the middle, and a bone incision is made in the posterior region of the mandibular angle, separating the inner surface from the outer surface. Following that, the lower jaw is freed and moved up and down or forward and backward to place it in its original and correct position. Plates and screws are used to maintain the mandibular bone in its new position.
Double jaw osteotomy is a surgery performed on both the upper and lower jaws. It is done when both jaws have problems, abnormalities, or disorders.
Genioplasty is a chin surgery that corrects chin defects and addresses backward or forward positioning of the chin bone. The chin, or specifically the mandible, is reconstructed by cutting the chin bone in front of the jaw and creating aesthetic improvements to the appearance of the chin.
If your gums are excessively visible when you smile, and your upper jaw is more prominent than normal, you may be a candidate for orthognathic jaw surgery. A certain degree of these gummy smiles can be corrected with gum and bone surgery. The patient can gain a beautiful smile without the need for jaw surgery. However, in broader cases, jaw surgery is necessary to achieve ideal aesthetic results. To address this issue and schedule a visit with Dr. Alireza Modaresi, a maxillofacial surgeon, please contact us.
Nutrition after Orthognathic Jaw Surgery (Orthosurgery)
Receiving sufficient protein and calories during the postoperative period is vital to counteract the catabolic metabolism that occurs as a response to the stress induced by the surgery.
The nutritional needs of the patient increase simultaneously with the temporary dysfunction of the jaws. Prolonged fixation of the upper jaw exacerbates the problem. Reasonable goals for calorie and protein intake are 2500 to 3000 calories per day and 1 to 1.5 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day.
Supplemental protein shakes may also be necessary. It may be recommended to receive nutritional counseling prior to hospitalization.
Having controlled care and nutrition in terms of calorie and fluid intake significantly contributes to the patient’s recovery process.

Factors that Require Orthognathic Surgery
- Malocclusion
- Protrusion or shortness of the face
- Excessive gum height
- Gum protrusion during smiling
- Open bite
- Asymmetry in the right and left jaws
- Congenital or genetic problems and insufficient jaw bone growth
- Retruded or protruded chin
- Swallowing or chewing difficulties
Postoperative Instructions of jaw (orthognathic) surgery:
- Rest is necessary for up to two weeks after jaw surgery.
- Take medications, mouthwash, and follow hygiene instructions precisely.
- Never change or discontinue your medications without consulting your doctor.
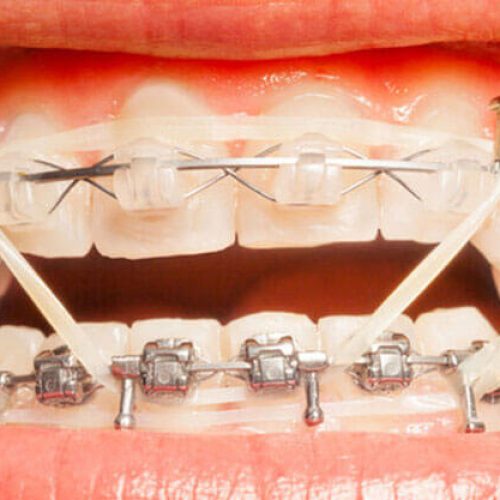
- Both jaws are connected with special wires after the double jaw surgery, so taking care of the wires and following hygiene instructions is crucial for your treatment and recovery.
- You will need a check-up one week after the surgery, so make prior arrangements to visit the clinic.
- Facial stitches are usually removed five to seven days after the surgery, and oral stitches are typically removed two weeks later.
- Avoid activities that make you lower your head or neck.
- Pain, swelling, bruising, redness, and discoloration of the face down to the throat are normal for up to two weeks after the surgery.
- Swelling or changes in the shape of the upper lip and nose are common and natural after the surgery, and they will gradually return to normal within two weeks.
- Numbness in facial areas (under the eyes, lower lip, upper lip, cheek, chin, etc.) and even in the teeth area is probable after the surgery, which is normal and will gradually return to normal over time.
- Apply ice compression on the facial area for up to 24 hours after the surgery. Place it on the face for about half an hour and remove it for approximately ten minutes. Repeat this process for 24 hours.
- Swallow your saliva after the surgery and avoid gargling or spitting for 24 hours.
- Nosebleeds may occur up to 72 hours after the surgery, and it is normal. Tilt your head slightly upward to control it.
- The presence of bleeding inside the mouth is normal for up to 72 hours after the surgery, but if you notice uncontrollable bleeding, inform your surgeon.
- Congestion, pinching, or closing of the nose after the surgery is normal and gradually returns to normal.
- Showering is allowed after the surgery, but during the initial 24 hours, only the body should be washed, and afterward, complete showering is permitted. However, avoid applying pressure on the facial area.
- After the surgery, both jaws are connected with wires or special elastics and the upper and lower jaws are closed together. Therefore, the post-surgery diet will be different.
- Some weight loss after the surgery is somewhat normal.
- When resting or sleeping, lie in a slightly inclined position and avoid sleeping on the right or left side of your face.
- Place your head slightly elevated above your body when resting or sleeping.
- Avoid any possibility of injury to the head, face, and neck.
- Avoid contact with heavy objects or any object that can exert pressure on the face.
- Avoid risky activities and heavy exercises for up to six months.
- Patient’s nutrition should consist only of liquids and should be administered through a syringe for up to three weeks. Therefore, prepare a gavage needle for easy feeding of the patient.
- Consume cold fluids for up to 48 hours after the surgery and refrain from consuming hot food or fluids separately.
- Bring any mixed food mentioned below in a liquid and blended form. This liquid food should be drawn into the gavage needle and placed beside the patient’s lips, and the contents of the needle should be emptied in the corner of the patient’s mouth (next to the teeth) so that the patient can swallow easily.
- The patient’s nutrition for the first two to three weeks after the surgery should consist of high-calorie and high-protein fluids such as soups, meat broth, muscle broth, stew broth, and similar nutritious materials that are mixed and in a liquid form.
- Consuming meat and chicken broth is effective in maintaining health and the recovery process.
- Drinking fluids such as natural fruit juices is beneficial for maintaining health and aiding the recovery process. Drinking pineapple juice has a significant impact on the recovery process.
- Due to increased fluid intake, there is a possibility of urination or diarrhea. In such cases, inform your surgeon.
- Constipation may also occur after the surgery. In this case, inform your surgeon.
- Follow the hygiene instructions carefully according to your physician orders as they are of utmost importance.
- Oral hygiene is crucial during the first two weeks after the surgery.
- Use 2% chlorhexidine mouthwash twice a day for two weeks and rinse your mouth with a serum mouthwash after each feeding throughout the day. Use a syringe for mouth rinsing. Fill the syringe with the liquid and carefully apply it inside the mouth to ensure thorough rinsing.
- For mouth rinsing, the patient’s lip is moved aside, and the inside of the mouth, wires, teeth, and stitches are thoroughly cleaned.
- Use a soft or extra-soft toothbrush to clean the surface of the wires and teeth several times a day.
- After the surgery, both jaws are temporarily closed. If the jaws are connected with elastics or intraoral rubber bands and specific bands are given to the patient, they should always carry these bands with them. If the jaws are connected with special wires, they should obtain wire cutters and keep them with them at all times so that in case of vomiting or preventing aspiration and fluid entering the lungs, they can cut the wires and open the jaws. Note that the process of opening the wires should only be done in emergencies and in case of vomiting. Therefore, it is essential to carry wire cutters everywhere and at all times, even when you go to the restroom or shower.
- In case of any emergency, inform your surgeon. If you cannot reach your surgeon for any reason, you can visit the hospital where the surgery was performed to address emergency situations.
- If you experience unusual and uncontrollable pain, excessive swelling, trauma, impact, or the sensation of dirt or infection inside the mouth, inform your maxillofacial surgeon immediately.
- Patients who underwent orthodontic treatment before jaw surgery should continue their treatment by visiting their orthodontist. However, they should be aware that unless their maxillofacial surgeon provides written approval for continuing orthodontic work, there is no need to visit their orthodontist.
- Preserving the dental relationship and occlusion of the patient’s jaws is crucial in this surgery. Therefore, if you feel any movement or misalignment in the relationship between the two jaws, inform your surgeon immediately.
- After opening the wires of both jaws, the mouth usually opens less than before. Functional limitations are natural for a while and gradually return to normal with the surgeon’s instructions.
How long does the recovery period after surgery take?
The patient is usually hospitalized for one to three days after the operation, depending on the type of surgery. Pain and swelling are normal for up to two to three weeks after the operation, but they are controlled with medication and instructions given by the surgeon. Carefully read the postoperative instructions to ensure a proper and accurate recovery process and prevent possible complications.
[read more]
The entire recovery period after jaw surgery takes about three to six months. From the second week onwards, you can return to work with the surgeon’s approval. However, if your job involves speaking or prolonged meetings, it is better to take one month off, as speaking with a closed mouth is not possible, and pressure should not be applied to the jaw.
After the surgery, retention appliances are used until you are referred to an orthodontist after a period of one month. The dietary guidelines after the operation are different, and you should consume only fluids for the first two weeks. Dry mouth is also commonly observed, but it is controlled by consuming fluids and following the surgeon’s instructions. Weight loss is commonly seen after any jaw surgery, which is a natural process due to nutritional control and, if enough protein and carbohydrates are consumed, this weight loss contributes to overall body health.
Sometimes, you may experience numbness in your upper or lower lip after the operation, which rarely occurs and is usually temporary, resolving within a few weeks or months. The recovery process takes about one to two months, and during this time, you should regularly schedule check-ups with the maxillofacial surgeon to assess the surgical stages and the healing of the area.
[/read]
Important factors for expediting the recovery of jaw surgery
Proper nutrition before and after the operation, protecting the bones and tissues of the surgical area in terms of blood supply to the connected and operated jaw, complete protection of the jaw and face to stabilize the fixed area and preserve the neural, vascular, and dental structures, cleaning and caring for intraoral wounds after the operation, etc. are very important until the jaw returns to its normal state.
Causes of Jaw Abnormalities
Genetic factors play a significant role in the formation of body bones, including the jawbone.
During the growth period, factors such as trauma and injury, sucking on pacifiers or fingers, tonsil problems, airway obstruction caused by tonsils and adenoids, dental abnormalities, premature loss of deciduous teeth, and failure to maintain space for permanent tooth eruption, etc., can lead to the occurrence of abnormalities and skeletal disorders of the jaw.
Apart from affecting the functional and health aspects of individuals, the mentioned factors also have a direct impact on the aesthetic appearance of individuals. Therefore, dental check-ups for children, preservation of deciduous teeth in their proper position until the eruption of permanent teeth and subsequent check-ups by an orthodontic specialist during adolescence, oral hygiene control, and prevention of dental complications play a significant role in maintaining the health of the jawbone.
What are the Complications of Jaw Surgery?
The following are some rare complications that are occasionally observed among patients and their occurrence depends on the type of surgery, surgical conditions, and the patient’s physical condition. Typically, these complications are temporary and controllable.
- Pain and swelling
- Facial and neck bruising
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Tingling and numbness
- Stiffness of jaw muscles
- Nasal congestion
- Weight loss
- Bad breath
- Dry mouth and tongue
- Bad breath
- Constipation
Cost of Jaw Surgery
The cost of jaw surgery, like other body surgeries, depends on various factors. These include the type of surgery, severity of skeletal jaw abnormalities, the chosen treatment location and hospital, duration of hospital stay, the specialization of the surgeon, surgical techniques and skills, the need for prosthetics and grafts, additional surgeries, consumables, etc. These factors directly impact the cost of the surgery.
The cost of jaw surgery in 1401 (2022/2023) starts from approximately 15 million tomans. After examining the patient’s clinical condition and reviewing radiographs, CT scans, and patient photos, the jaw and facial surgeon determines the treatment plan and provides information on the treatment process and associated costs based on the type of surgery.
To schedule a consultation and appointment, please contact our reception.