Reconstructive Bone Surgery in the Jaw
In almost all restorative or cosmetic surgeries in the jaw, the density of bone at the site of the procedure plays a crucial role in the treatment process, stability, and patient’s functionality.
This surgery may involve various bone grafts to reconstruct a small or large portion of the jaw or face, especially when there is significant bone destruction and loss.
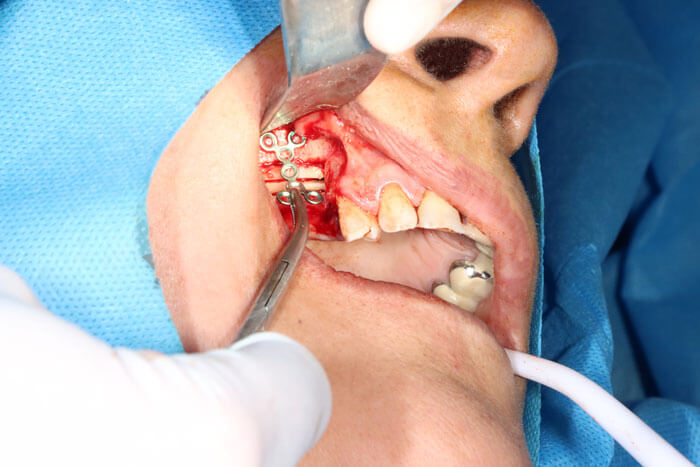
Lateral Augmentation
Lateral augmentation surgery is performed in the narrow ridge following severe horizontal bone resorption. There are three types of bone reconstructive surgeries within this category, which will be discussed below.
- GBR
- Bone block
- Ridge split
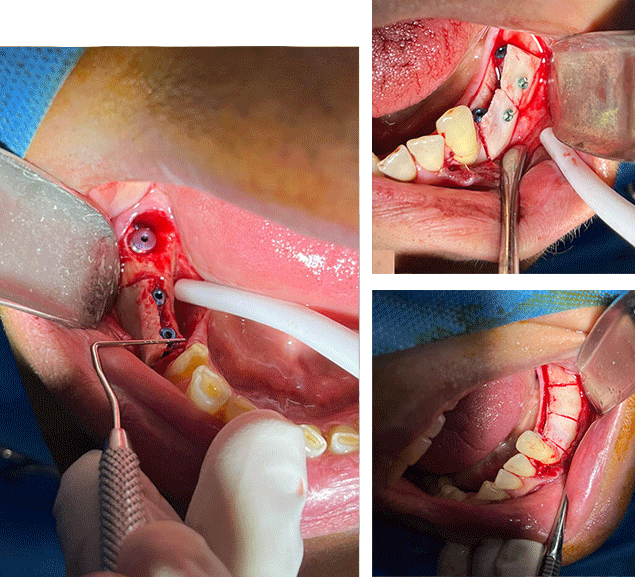
- GBR
- Bone block
- Ridge split
This treatment involves the use of bone powders or membranes for bone defect reconstruction in the jaw. The advantage of this method is that, it allows us to obtain and utilize the necessary volume based on the extent of bone resorption in the area. This treatment also includes various techniques such as autografts, allografts, xenografts, or a combination of them, as previously mentioned in the bone grafting section.
It involves harvesting a bone segment from the posterior region of the mandible or chin (from the patient’s own body) or using an allograft and placing it in the lateral area of the resorbed bone. The dimensions of the bone block can vary (depending on the needs of the resorbed area).
Fixation of this fragment to the bone is performed using screws and plates. In cases where there is severe and extensive resorption in the entire upper or lower jaw, bone blocks from the patient’s own iliac bone or bone blocks from the patient’s pelvis can be used for treatment, which is usually performed in the operating room under anesthesia.
This type of jaw bone reconstruction is the best and most effective method for lateral reconstruction. In this technique, specialized and delicate surgical instruments such as piezo saws and osteotomes are used to cut and open the targeted bone area from the horizontal midpoint. Typically, dental implants are placed simultaneously during this surgery, and the surrounding area is filled with bone grafts and bone substitutes.
This is a highly precise and sensitive technique, especially in the lower jaw. Its results are significantly better than other techniques, with a faster recovery and bone fusion process. With this method, it is possible to increase the width of the bone by approximately 5 to 8 millimeters.
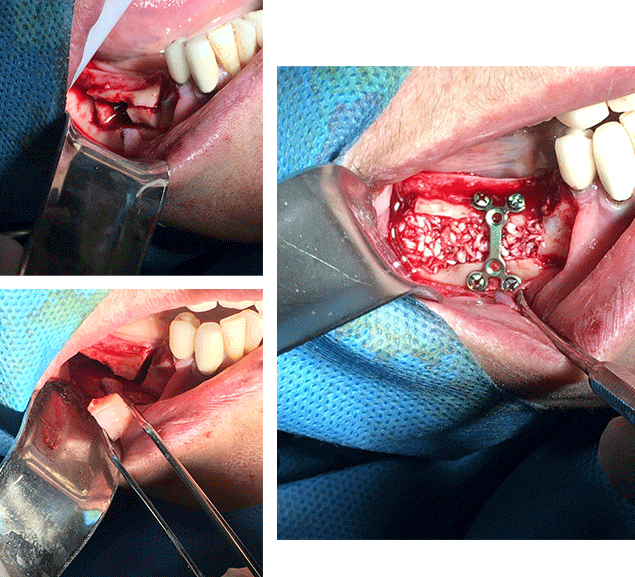
Vertical Bone Augmentation Surgery
Vertical augmentation
This surgery, which increases the vertical length of the bone, can be performed using three techniques and methods.
- GBR
- Bone block
- Sandwich Technique
- GBR
- Bone block
- Sandwich Technique
In this technique, similar to GBR in the field of lateral augmentation, bone powders, membranes, and tent screws are used to increase the volume of the bone. It is commonly used in cases with broader ridges.
In this method, as explained earlier in the section on lateral augmentation, bone blocks of different sizes are used at the ridge crest, and fixation to the jawbone is done using screws and plates.
The interpositional method is one of the best and most definitive reconstruction techniques for the posterior mandible. In this surgery, the bone is horizontally divided into two parts while maintaining careful preservation of blood supply through adherent soft tissues and displacing the bone upwards. Bone blocks and powders are then used to fill the created space between the two divided bones, and ultimately, the grafted piece is fixed to the jawbone using micro or mini plates.
This surgery is also performed using precise and delicate surgical instruments such as piezo surgery unit to minimize damage to soft tissues and achieve higher treatment quality.
In this technique, which creates the best results for bone reconstruction, it is possible to increase the height of the bone by approximately 10 to 12 millimeters. Typically, 3 to 4 months after vertical bone reconstruction surgery, the screws and plates used for fixation are removed, and then dental implant surgery begins.
Nerve lateralization
Lateralization and displacement of the inferior alveolar nerve is a suitable treatment method for patients who have a short bone height in the edentulous area and require dental implants. If we want to place an implant with the appropriate length and diameter for stability and better function in these individuals, it may encounter the inferior alveolar nerve, risking the treatment, or the analysis of the lower jaw bone in the posterior region can lead to a reduction in the bone edge and jeopardize implant placement.
This mostly occurs in the region of the sixth and seventh teeth. Nerve lateralization and subsequent implant placement in the atrophic posterior mandible are a solution for these patients. This is called nerve lateralization surgery.
Of course, there are several treatment methods for these cases, such as using short implants, bone reconstruction and grafting, placing implants at steeper angles, or inferior alveolar nerve displacement and lateralization.
This surgery is very precise and delicate and should only be performed by a maxillofacial surgeon specialist, and careful considerations should be made during the nerve displacement to preserve the sensory function of the lip. This technique allows for the use of longer implants and suitable prosthetic length compared to using shorter implants, for the preservation of the mandibular canal and better stability and functionality.
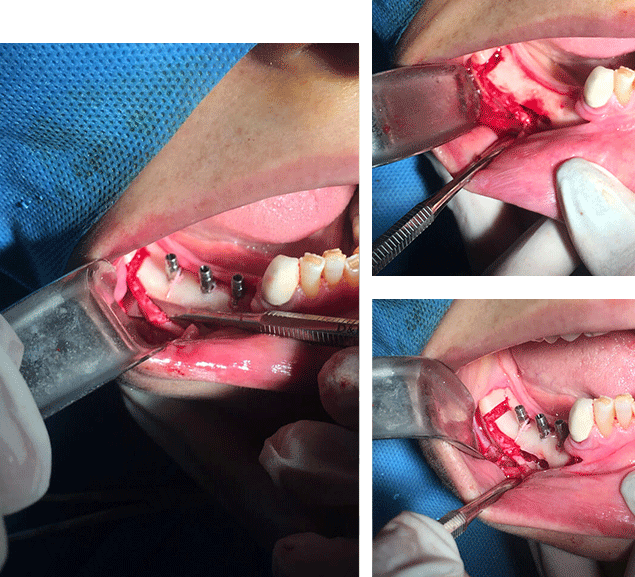
Jaw Bone Reconstruction
Patients who have lost their teeth for a long time suffer from jaw bone resorption, and since we need an appropriate tissue bed of hard and soft tissue for implant placement with ideal length and diameter, bone reconstruction is necessary. For consultation and treatment planning regarding jaw reconstruction methods, please contact our reception.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
- Saturdays: 14:00 to 20:00 - Punak clinic
- Sundays: 14:00 to 20:00 - Shariati clinic
- Mondays: 14:00 to 20:00 - Punak clinic
- Thursday: 14:00 to 20:00 - Saveh clinic
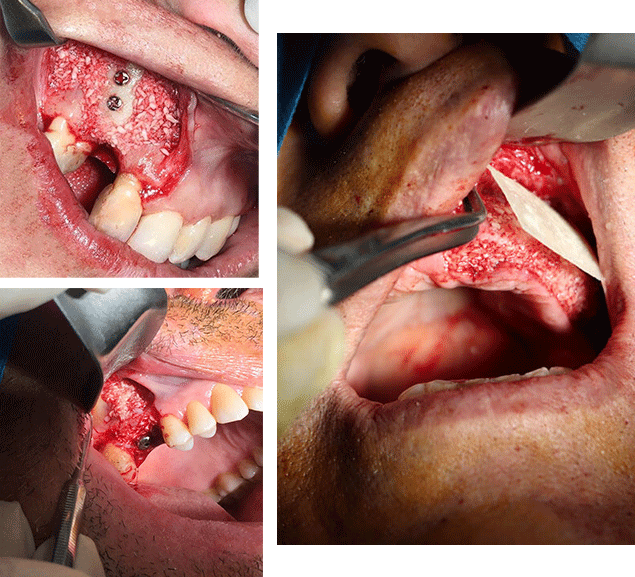
Bone Grafting
Bone grafting is a process in which damaged bone tissue is converted into strong and new bone tissue using grafting techniques and the use of bone graft materials.
Maxillofacial surgeons successfully utilize soft or hard tissue grafting techniques to transfer tissue from one part of the body to another that has experienced degradation.
This surgery can involve various bone grafts for the reconstruction of a small or large portion of the jaw or face. If the degree of bone destruction and degradation is significant, bone tissue for grafting is taken from the hip or leg and transferred to the jaw or neck.
Alternatively, if the bone graft is intended for a smaller area of the jaw, a piece of bone is taken from the end of the jaw or a portion of the lower jaw with good bone density and grafted in the desired location. If bone grafting is required with the use of powder or pre-made materials, the grafting is performed with the help of allografts, and the targeted area is reconstructed with bone grafting powder.
In general, three important factors are present in the stabilization and success of any bone graft:
- Induction of bone formation
- Bone vascularization
- Bone growth factors
Jaw Bone Grafting
In oral surgeries, the likelihood of tooth retention decreases when deep dental caries, infections, inflammation around the gums or root end, excessive pocket depth in the gums, plaque index, and loss of gum attachment become active. After tooth extraction, if conditions are suitable, it is preferable to perform dental implant placement simultaneously to prevent bone resorption in that area and fill the space left by the missing tooth more quickly. In the human body’s physiological system, when an organ is not used, it gradually loses its ability and functionality. After tooth extraction, if a toothless area remains without an implant, bone resorption begins gradually in the coming years.
[read more]
Teeth and the bone and gum surrounding them have complementary roles in the growth and health of each other. The presence of healthy teeth and roots inside the jawbone helps to maintain the health and density of the bone tissue, and on the other hand, the presence of healthy bone and gum, free from lesions and masses, is very effective in preserving the tooth and its root. Therefore, any form of decay, trauma, injury, infection, inflammation, mass, tumor, or pathological lesions of this nature may damage the tooth and the supporting bone around it.
Dental roots play an important role in maintaining and activating bone cells. If a tooth is lost for any reason, the activity of cells for preserving and maintaining bone volume is also lost, and this is where the process of jawbone resorption begins. This resorption occurs later and more slowly in adolescents and young adults due to physical growth conditions. However, it is more rapidly in middle-aged individuals. This resorption may occur in the width, length, or volume of the bone.
This event mostly occurs in the area of the sixth and seventh teeth, and the lateralization of the inferior alveolar nerve and subsequent placement of implants in the posterior atrophic mandible is a solution for these patients. This is called nerve lateralization surgery.
Of course, there are several treatment methods for these cases such as using short implants, bone reconstruction and grafting, placing implants at steeper angles, or the displacement of the inferior alveolar nerve and lateralization.
This surgery is very precise and delicate and should only be performed by a maxillofacial surgeon, and precise considerations should be made during nerve displacement to preserve lip sensation. This technique allows for the use of longer implants and prostheses compared to using shorter implants in order to preserve the lower jaw canal and achieve better stability and functionality.
[/read]
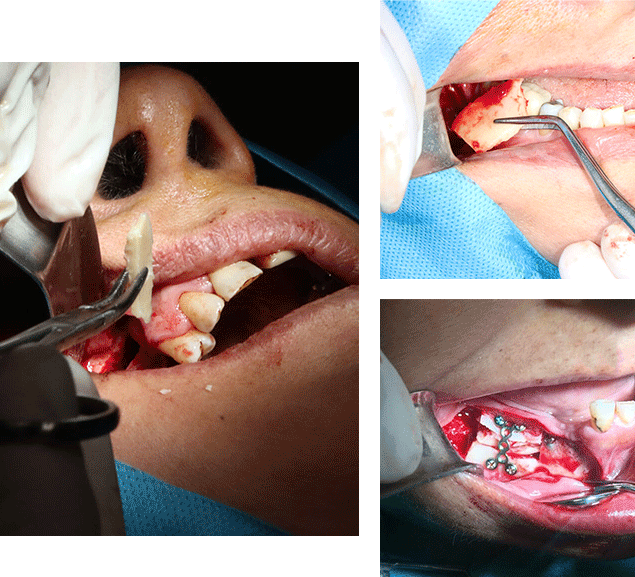
Types of Bone Grafts
- Autografts
- Allografts
- Xenografts
- Alloplasts
Autografts, also known as autogenous bone grafts, are one of the most effective types of grafts for the purpose of augmenting a depleted area. In autografts, bone is harvested from the individual’s own body and transplanted to the desired site. Due to the use of the individual’s own bone as the graft material, autografts offer faster and more successful integration compared to other types of grafts. The body’s own bone serves as a good source of the individual’s own cells, reducing the risk of graft rejection by the immune system. Bone reconstruction in the jaw is necessary for patients who have suffered extensive tooth loss, as an ideal implant placement requires a suitable foundation of hard and soft tissue. For consultation and treatment planning regarding jaw reconstruction methods, please contact us to schedule an appointment.
Allografts, also referred to as allogeneic grafts, involve the use of tissue or bone donated by another human or obtained from a bone bank. These grafts are used in the intended area for transplantation.
Allografts typically require a longer integration period compared to autografts, as it takes time for them to fuse with the body’s tissue. However, they have the advantage of providing larger volumes for grafting in extensive surgeries or in areas that require extensive reconstruction of soft or hard tissue. Therefore, they are a suitable option for individuals with severe bone loss.
Xenografts utilize animal-derived sources for bone grafting. The main source of xenografts is bovine bone, which is harvested and transplanted as grafts.
In xenografts, the animal bone gradually integrates with the individual’s own bone tissue and replaces it over time.
It is a type of graft or transplant in which an artificial bone is employed as a substitute, chemically resembling human bone. It stimulates and activates the individual’s bone cells through a base of calcium phosphate and tricalcium phosphate, providing a suitable environment for the formation of new bone cells and grafting to the desired area.
Facial Organ or Tissue Grafting
1. استئوبلاست ها در فرایند استخوان سازی نقش به سزایی دارند و باید در محل وجود داشته باشند. استئوبلاستها از شبکه های چین خورده فراوانی که غشای نازکی دور آن را گرفته تشکیل شده که این اندوپلاسما پروتین و کربوهیدراتها را به اندامکهای سیتوپلاسمی و غشای سلولی منتقل میکند. این شبکه با ترشحات خود باعث میشود استئوپلاستها در استخوان ذخیره شوند و با تراکم خود به فرآیند پیوند استخوان کمک کنند.
2. خونرسانی باید در محل وجود داشته باشد. خون برای تغذیه استخوانی به میزان کافی باشد. وجود خون و درامتداد آن به وجود آمدن لخته های خونی محل مناسبی برای رشد استئوپلاستها میباشد.
3. ثبات اولیه در پیوند انجام شده از فاکتور های مهم پیوند است. پیوند باید در طول بهبودی تثبیت شود. هر گونه فشار و حرکت در بافت پیوندی منجر به شکست درمان میشود بنابراین در برخی از جراحیها ممکن است جراح از پیچ و پلیتها جهت فیکساسیون ناحیه استفاده کند.
4. بافت نرم باید حفظ شود و بدون اسیب باقی بماند. نباید تحت کشش باشد. غشای نازک بافت نرم مانند عایقی برای تشکیل و پیوند استخوان عمل میکند پس هرگونه آسیب به سطح بافت نرم ممکن است، عملکرد و فرم استخوان پیوند شده را تحریک یا تغییر دهد.
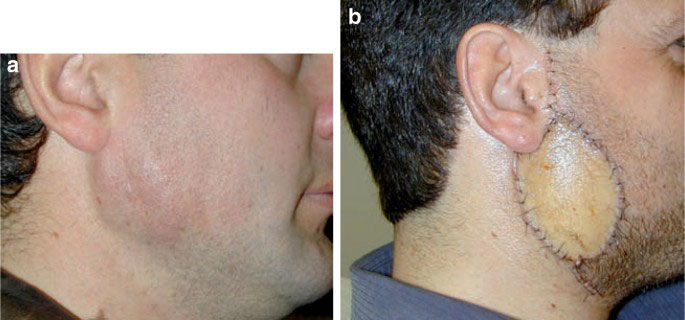
Facial Organ or Tissue Grafting
In cases of traumatic patients or individuals who have lost a portion of their facial or neck structure in sudden accidents, facial organ or tissue grafting is performed, including bone grafting, soft tissue grafting, or a combination of both in more extensive injuries.
Understanding facial anatomy and analyzing the condition of healthy tissues, and the surgical techniques and skills play a crucial role in the grafting process. It significantly contributes to the treatment, functionality, and aesthetic aspects of the organ. Utilizing a combination of medical techniques and artistic skills, this surgery offers ideal long-term results.
Typically, in cases of extensive damage, after initial reconstruction procedures, an oral and maxillofacial surgeon seeks consultation from a plastic surgeon or a specialist in dermatology and hair. Alternatively, in more severe stages, following the grafting procedure and recovery of the graft site, the patient may be referred to a plastic surgeon for skin and soft tissue reconstruction.