Surgical Treatment of Impacted Teeth
An impacted tooth is a tooth that has not emerged properly during its original growth and has remained beneath the bone and gum, returning to a dental arch. There are various reasons why a tooth may remain impacted within the bone. In 90% of cases, impacted teeth need to be surgically removed.
Why does an impacted tooth remain in the jaw?
Sometimes, primary or permanent teeth become impacted due to improper growth and eruption, ankylosis, or failure to rotate vertically in an impacted position. In such cases, with the opinion of an orthodontic specialist and a maxillofacial surgeon, if there is a possibility to reposition the tooth to its original position within the dental arch through modern orthodontic methods and with the help of surgical procedures to open up the bone space, it can be done.
However, this treatment method depends on the location of the impacted tooth and the shape of its roots, and it is not feasible in all cases. Nevertheless, if approved by an orthodontic specialist, this method is a suitable solution for extracting impacted teeth since the natural tooth is worth the functionality and preservation.
If the impacted tooth cannot be brought out through orthodontic treatments and has significant disadvantages due to its shape and position, then surgical extraction of the impacted tooth must be performed.
It is possible that all of a person’s primary teeth have erupted and grown fully, and there is no deficiency in the number of primary teeth. However, when a dental radiograph of the jaw is taken, it is discovered that there is an impacted tooth within the jawbone, which is an additional impacted tooth.
All additional teeth, whether impacted or not, must be removed. An additional tooth hinders the growth and eruption of permanent teeth and may alter the eruption site of primary teeth. Therefore, an additional tooth must be extracted.
Impacted teeth often become cystic and can destroy the roots of adjacent teeth. In more severe cases, they can develop into tumors or ameloblastomas and erode the jawbone.
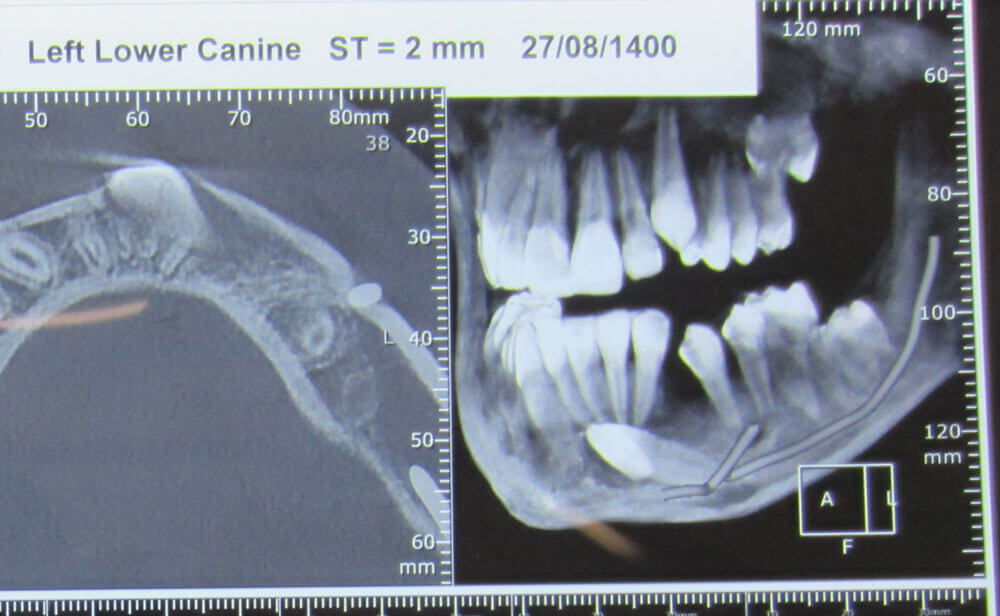
CT Scan for Evaluating Impacted Teeth
Removing impacted teeth has its own specific complexities and requires a high level of skill. Access to the area, the space within the mouth and jaw, the patient’s physical conditions, the positioning of the roots of impacted teeth, proximity to the sinus, the shape of the roots of adjacent teeth, etc. are all important factors that necessitate the expertise and advanced techniques of a maxillofacial surgeon for the extraction of these teeth. After examining the patient’s OPG radiograph, the maxillofacial surgeon may prescribe a CT scan of the jawbone to precisely evaluate the length, diameter, and exact location of the impacted tooth and its roots in three dimensions. This allows for accurate treatment planning and precise execution of the treatment, thereby preventing potential damage to the jaw, nerves, sinuses, and the adjacent teeth.
Surgical Treatment of Impacted Teeth
One of the complications of removing impacted teeth in the upper jaw, particularly those close to or involving the sinus, is the opening of the sinus and the formation of an oro-antral fistula. If you are facing this problem, you can consult our maxillofacial surgeon.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
- Saturdays: 14:00 to 20:00 - Punak clinic
- Sundays: 14:00 to 20:00 - Shariati clinic
- Mondays: 14:00 to 20:00 - Punak clinic
- Thursday: 14:00 to 20:00 - Saveh clinic
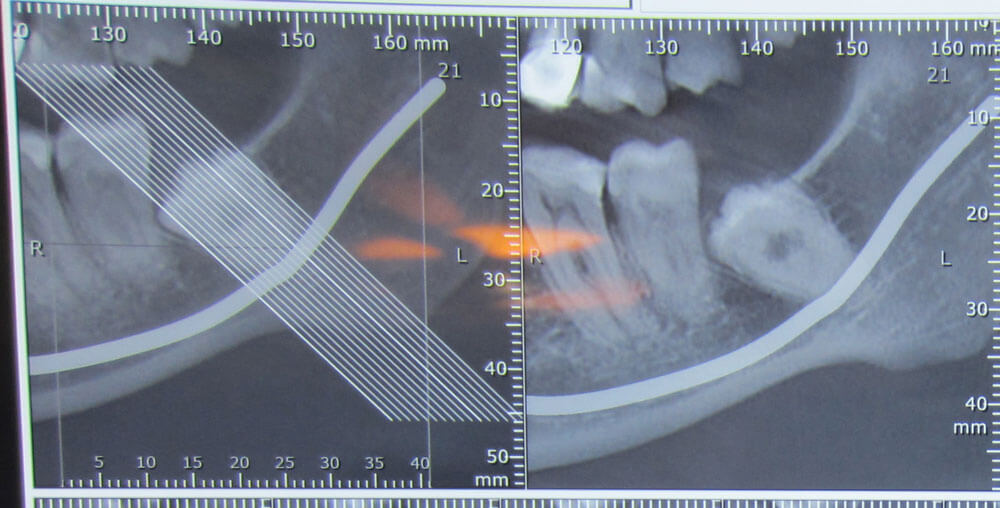
Impacted Tooth Involving the Inferior Alveolar Nerve
If a tooth requires extraction and radiographic observations reveal that the crown or root of the tooth is in close proximity to or has impinged upon the main jaw nerve or the inferior alveolar nerve, the surgical procedure will be more complex, and the extraction techniques will be different. Therefore, one of the most significant complications of extracting these teeth is damage to the inferior alveolar nerve.
During this process, as the tooth and root are lifted off the nerve, the nerve may come under pressure or traction, leading to temporary or long-term numbness of the lip. This nerve is responsible for providing sensation to the lip. Therefore, if, for any reason, the inferior alveolar nerve is damaged during surgery, the resulting complications may include lip numbness or paresthesia, tingling sensations in and around the lip, both in the short or long term.
Potential Complications of Nerve-Related Dental Surgery
This nerve is not responsible for facial movement. Therefore, in case of nerve damage, the patient does not experience lip, jaw or facial dysfunction or facial paralysis. However, the most noticeable complication of dental surgery involving the root or the proximity of the nerve is numbness of the lip and the surrounding skin.
In some cases, the sensation can return to the lip and the surrounding skin with medication, laser therapy, repeated check-ups, and controlling the patient’s condition. However, depending on the type of surgery and the positioning of the tooth root, this numbness may be permanent.
[read more]
Considering all the possibilities and complications associated with the extraction of the impacted teeth, leaving these teeth in the jawbone may lead to various other problems and increase the likelihood of cyst formation and the development of masses in the jaw. Therefore, any impacted tooth should be surgically removed during adolescence and young adulthood.
Regarding root or crown involvement with the nerve, this treatment should only be performed by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
By carefully examining the patient’s CBCT of the jaw, the specialist analyzes the positioning and the type of nerve involvement and plans the treatment and surgical procedures using their specific techniques and skills, aiming to avoid nerve irritation or minimize damage to the dental nerve during extraction.
Of course, depending on the location of the impacted tooth, it may not be practically possible to perform surgery without damaging the nerve. Therefore, everything depends on the opinion and treatment plan of the oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
Another nerve, known as the lingual nerve, plays a role in tongue sensation. Potential surgical complications may also lead to numbness of the tongue. If either of these two nerves is affected or damaged, depending on the type of surgery and the positioning of the tooth roots and their relationship with the nerve, numbness, tingling, and paresthesia may occur in the lip, tongue, and the skin around the chin.
The nature of nerve disorders and the type of trauma have an impact on the decision-making process for treating this condition. These symptoms are sometimes temporary and gradually resolve within two to six months, while in other cases, they may be permanent and long-lasting. Typically, they are managed and controlled with care instructions and medication, leading to a process of improvement. However, if there is significant destructive effect, laser therapy may also be prescribed.
[/read]
Post-operative Care for Impacted Tooth Surgery
- If a sterile gas has been placed at the surgical site at the end of the surgery, firmly bite on it with your teeth for up to one hour. Then gently remove the gas and consume cool juice or ice cream.
- Try to limit talking, especially during the first four hours after surgery.
- Some slight bleeding and red-tinted saliva may occur from the surgical site for up to two days, which is not a cause for concern.
- Avoid drinking with a straw, chewing, or spitting for the first two days.
- Refrain from engaging in heavy lifting and bending down for the first two days.
- Avoid consuming hot foods for the first two days and opt for cold or lukewarm foods.
- Avoid exercising, going to the swimming pool, or sauna for the first two days.
- Do not smoke for the first two days.
- Avoid touching the surgical site with your tongue and avoid contact with the sutures.
- Make sure to consume nutritious meals and plenty of fluids, as well as nourishing snacks.
- It is better to consume soft foods and avoid chips, nuts, and similar items.
- If you feel that the sutures have come undone, contact the clinic for guidance.
- Place your head slightly elevated during sleep for the first 24 hours after surgery.
- Oral hygiene is extremely important during the first week after surgery.
- Brush your entire mouth except for the surgical area from the day after surgery.
- Do not brush your teeth on the first night of surgery. You may start using a toothbrush and mouthwash 24 hours after surgery and continue for one week.
- Use chlorhexidine mouthwash every 12 hours and only use it as prescribed by the doctor. Consult your doctor if you need to continue using this mouthwash for more than one week.
- You can gently rinse the surgical area using a syringe filled with saline solution.
- Take your medications according to the instructions and at the specified times.
- Use an ice pack on the surgical site for ten minutes at a time, with intervals of half an hour, for up to 24 hours.
- Swelling of the face, bruising, and limited mouth opening are possible, and they may increase for up to three days and gradually return to normal after three days.
- Your breath may not be pleasant for approximately one week, and you may experience a bad taste.
- If swelling or pain worsens after the fourth day following surgery, make sure to seek medical attention. If you are taking other medications for other medical conditions, inform your surgeon.