Wisdom Tooth Surgery
Wisdom teeth sometimes grow like other teeth and are positioned next to the other teeth on the jawbone. Sometimes they are hidden or partially hidden inside the bone and below the remaining gum, causing hidden or visible complications for the individual.
If the patient’s mouth provides sufficient space for the growth and placement of the wisdom tooth, and if it does not exert pressure on the adjacent teeth and has an opposing tooth in the upper jaw that creates an appropriate biting surface for the patient, there is a possibility of retaining this tooth under such conditions. However, if these conditions are not met, one should consider the surgery to remove the wisdom tooth.
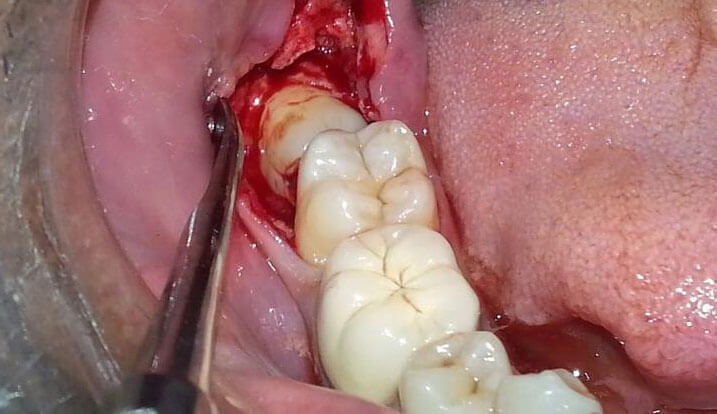

Why should wisdom teeth be surgically removed?
Usually, oral and maxillofacial surgeons recommend the extraction of wisdom teeth through surgery. Access to the back of the mouth and the location of the wisdom tooth is very difficult, making it impossible to maintain hygiene in that area, resulting in the migration of oral bacteria. Therefore, after the occurrence of decay, there is a possibility of damage and decay of the adjacent teeth and molar teeth in the jaw. After the formation of lesions and infections around the wisdom tooth, the surgical conditions become more complicated and in some cases, if the lesion and infection progress, there may be a need for hospitalization and more extensive measures.
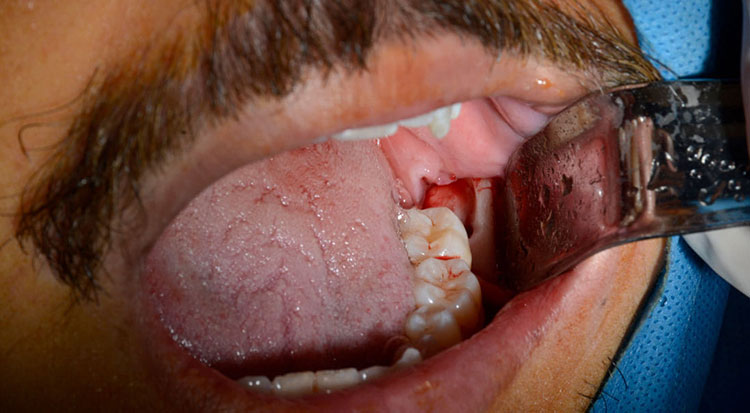
The main reasons for the need to surgically removing wisdom teeth
In some cases, the wisdom tooth has fully grown and has suitable visual conditions, but due to the small space in the jaw, wisdom tooth extraction is necessary.
Sometimes the wisdom tooth has fully grown and appears healthy like other teeth, but due to the pressure on the other teeth, it causes dental misalignment, requiring wisdom tooth surgery.
Sometimes the wisdom tooth has fully grown and has a healthy appearance similar to other teeth, but due to its location at the back of the mouth, it is not accessible for proper brushing and the use of dental floss, leading to the prevention of food accumulation, plaque formation, and infection, thus requiring wisdom tooth surgery.
Sometimes the wisdom tooth has a healthy and appropriate shape, but its roots, which are inside the bone, have abnormal shapes, improper placement, or incomplete growth that cause problems and infections and require wisdom tooth surgery.
Sometimes the root of the wisdom tooth, which is inside the bone, is affected by a lesion, cyst, or infection, necessitating wisdom tooth surgery.
Sometimes the wisdom tooth is hidden or partially hidden inside the bone or below the gum, requiring wisdom tooth surgery to prevent any complications and infections.
Sometimes the wisdom tooth inflames and affects the surrounding gums and adjacent teeth, necessitating wisdom tooth surgery.
Sometimes the wisdom tooth is decayed and requires root canal treatment, but due to the shape and position of its roots and the space of the tooth, it is not possible to perform root canal treatment, thus requiring wisdom tooth surgery.
Sometimes the wisdom tooth does not exist in the opposing jaw and essentially has no impact on the patient’s biting and chewing, requiring wisdom tooth surgery.
Wisdom tooth surgery is performed to prevent decay of the adjacent teeth.
Wisdom tooth surgery is performed to prevent pericoronitis.
Wisdom tooth surgery is performed to prevent the breakdown of the adjacent tooth roots.
Wisdom tooth surgery is performed to prevent impaction pain and temporomandibular joint problems.
Wisdom tooth surgery is performed to prepare the mouth and teeth for orthodontic treatment and to resolve dental misalignment.
The extraction of impacted teeth can be either simple or very complex, depending on the location and root of the tooth. All impacted teeth must be removed. In other words, all impacted teeth have the potential for bone destruction, cysts, lesions, tumors, abscesses, and infections, and must be removed surgically. Therefore, in patients with pathological symptoms, the extraction of the tooth is necessary according to the diagnosis of an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
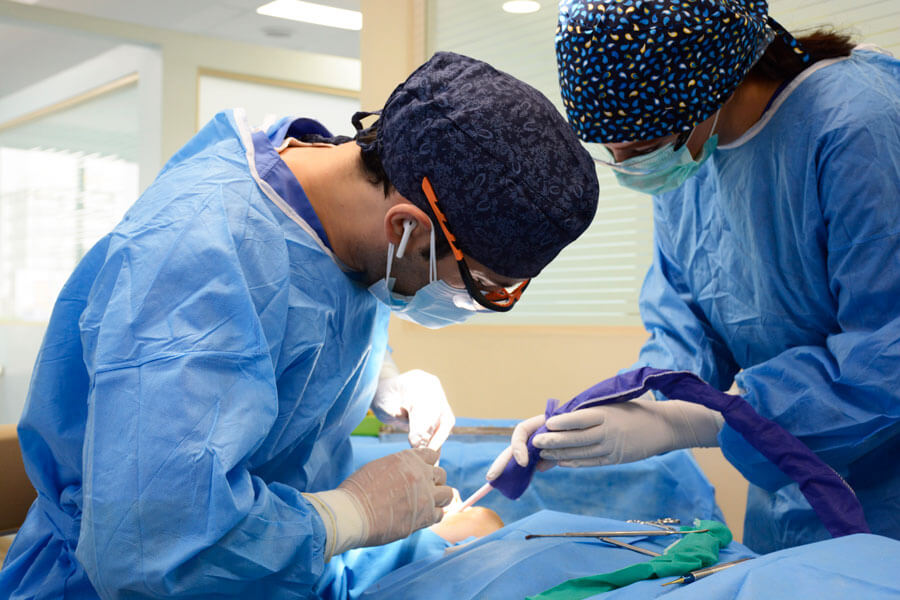
Wisdom Tooth Surgery under Anesthesia
Wisdom tooth surgery, as well as other impacted teeth, can be performed under anesthesia. Since tooth extraction surgery can be stressful and worrisome for some patients, especially those with dental phobia, who may have significant anxiety and hinder the treatment due to severe stress and lack of cooperation, it is better to perform surgical treatment under anesthesia for this group of patients.
Anesthesia is a last resort. There are cost-effective ways to control patient anxiety and stress before starting the surgery, so that both the surgeon and the patient can undergo treatment in complete calmness and in the best possible manner.
The maxillofacial surgeon controls your stress by prescribing sedative drugs at different doses and using anxiety control medications before starting the treatment. During the procedure, they administer appropriate and proper general anesthesia to ensure that the patient does not experience any pain during the treatment. With their specific techniques and expertise, they remove the tooth in a way that the patient does not experience any physical or psychological harm.
However, despite all these conditions, it is still possible that some patients are not adequately controlled with medication or personally request treatment under anesthesia. In such cases, the maxillofacial surgeon usually recommends removing all four wisdom teeth in one session so that the patient does not require anesthesia again for the removal of opposing wisdom teeth, and the time, medication, and post-treatment rest can all be done at once. In wisdom tooth surgery under anesthesia, the anesthesia costs are calculated separately from the treatment costs.
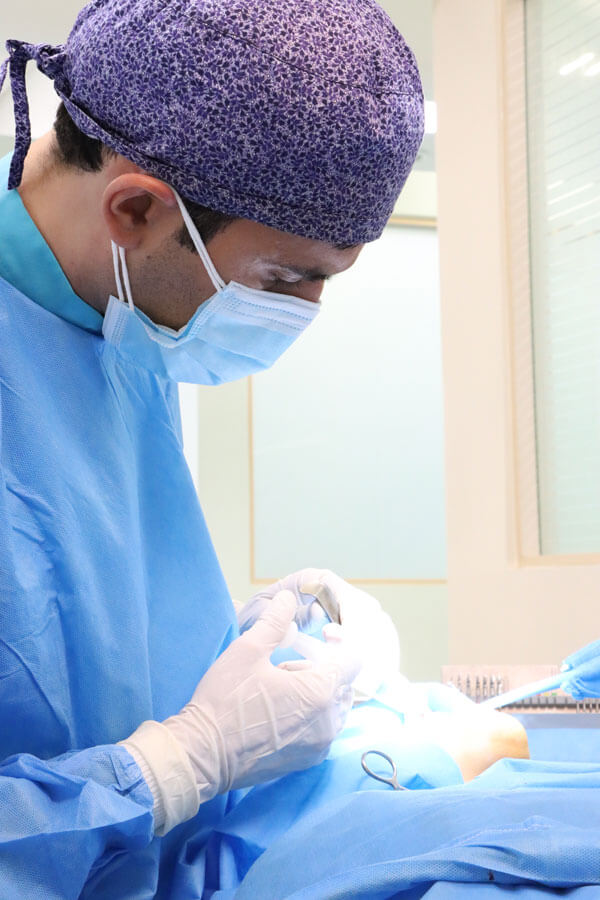
- Impacted Tooth Involving the Inferior Alveolar Nerve
If a tooth needs to be extracted and radiographic findings indicate that the crown or root of the tooth is close to or in contact with the main inferior alveolar nerve or the inferior alveolar nerve canal, the surgery will be more complex, and the techniques for tooth extraction will be different.
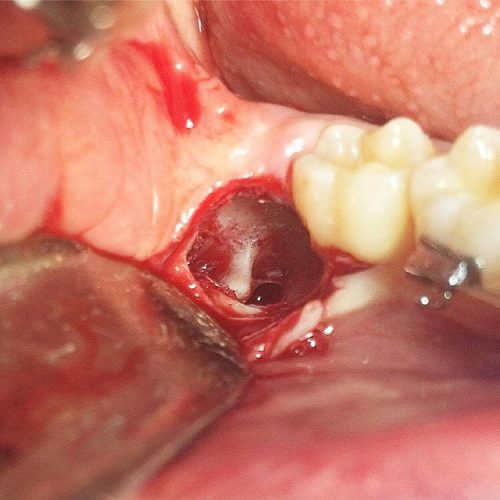
How is Wisdom Tooth Surgery Performed?
If the maxillofacial surgeon recommends extracting the wisdom tooth and if your wisdom tooth has grown correctly, does not involve the inferior alveolar nerve, and if it does not have complex roots within the bone, then it can be removed by conventional methods such as pulling it out.
However, if the tooth is in an improper position, has extensive decay, has curved or long roots, involves the nerve, or is partially or fully impacted, it definitely needs to be surgically removed.
In the wisdom tooth surgery process, after administering local anesthesia to the teeth or the entire jaw, the maxillofacial surgeon ensures numbness and creates an incision on the gum surface to gain access to the tooth.
In the case of impacted teeth within the bone, it is necessary to remove a small amount of the surrounding bone to access the crown and root embedded in the bone. Then, the tooth is divided into small pieces and removed from the site.
Once the impacted or partially impacted wisdom tooth is successfully removed, the surgical site is sutured.
What is the appropriate age for wisdom tooth surgery?
After the completion of the adolescent period, the roots of permanent teeth, including wisdom teeth, gradually mature, and the best time for wisdom tooth extraction is between the ages of 17 and 25.
Depending on the condition and position of the teeth, surgery can also be performed at older ages, but the treatment conditions become more challenging. Younger patients tolerate surgery better, have more favorable treatment outcomes, and experience faster recovery.
During the growth of the tooth crown and root, the position of the teeth can also change. If the wisdom tooth does not have suitable conditions for growth and does not occupy the proper position, it can cause problems in the surrounding gums, bone, and tooth root, which may require surgical removal.
[read more]
Sometimes at initial stages, these problems manifest as swelling and infection on the gums or face, and the patient becomes aware of the symptoms. However, in some cases, the patient may not be able to detect the issue due to lack of pain and swelling, and it is only through dental check-ups that the dentist, upon seeing dental X-rays, may realize that both the root tip of the wisdom tooth and the supporting bone and even the adjacent teeth are affected by a mass, cyst, or bone lesion. This happens due to lack of attention to the impacted wisdom tooth and the need for its extraction through surgery. In such cases, depending on the condition of the tooth and root, the process of extracting becomes more complicated.
Therefore, in addition to regular dental check-ups, do not forget the necessity of visiting an oral and maxillofacial surgeon for the evaluation of wisdom teeth in the early stages of youth.
[/read]
Wisdom Tooth Surgery
If you have an impacted wisdom tooth with nerve involvement and have been referred to an oral and maxillofacial surgeon by other dental colleagues, you can contact the surgeon’s office for appointment coordination.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
- Saturdays: 14:00 to 20:00 - Punak clinic
- Sundays: 14:00 to 20:00 - Shariati clinic
- Mondays: 14:00 to 20:00 - Punak clinic
- Thursday: 14:00 to 20:00 - Saveh clinic
When is wisdom tooth extraction not recommended?
Complications of Retaining Wisdom Teeth
Due to their location and incomplete growth within the jawbone, they mostly become cystic and cause lesions, posing a risk to the health of the surrounding bone and adjacent teeth roots. If they are impacted, sometimes the patient is unaware of the presence of these impacted teeth inside the jawbone until they experience the first signs and symptoms. The accumulation of food debris and plaque behind the wisdom tooth increases the risk of decay, and due to poor access to the back of the mouth, flossing and brushing will also be challenging. Consequently, it is advisable to consult with an oral and maxillofacial surgeon regarding the necessity of extracting your wisdom teeth to prevent potential problems. The complications of retaining wisdom teeth include:
- Periodontal Diseases
- Pericoronitis
- Decay of Adjacent Teeth
- Cysts, Tumors, and Lesions
- Soft Tissue Infection and Cellulitis
Following gingivitis, even at mild conditions, bacteria reach and invade the root surface, leading to mild or advanced periodontitis.
When a semi-impacted or impacted wisdom tooth becomes inflamed, a significant amount of soft tissue at the back of the mouth swells. With the accumulation of food debris under the operculum and bacteria beneath this soft tissue and gum, an infection develops, leading to the phase of pericoronitis. Pericoronitis is an infection of the soft tissue around the crown of the tooth, which is commonly observed behind the wisdom tooth.
Due to the pressure exerted by the wisdom tooth and the accumulation of bacteria under and around the supporting gum, the maintenance of oral hygiene in that area becomes challenging. During eating, food particles may get stuck between the adjacent teeth and beneath the gum, forming a pocket and causing decay and bone and gum breakdown, leading to the destruction of the molar teeth, mainly due to the positioning of the wisdom tooth.
In many cases, the roots of wisdom teeth inside the jawbone develop cysts and become infected, causing significant pain and inflammation.
Wisdom teeth can cause inflammation and bacterial infection in the throat, tongue, and cheek.
- Osteomyelitis
- Abscess
- Root Resorption
- Temporomandibular Joint Pressure
Osteomyelitis is a bone infection that requires antibiotic treatment as soon as its initial symptoms appear and sometimes even surgical intervention. The infection reaches the bone through nearby tissues or blood supply. Sometimes, due to an injury, the bone becomes susceptible to microbial accumulation and subsequently develops an infection within the bone itself.
Bacteria and plaque that accumulate around the gum and tooth crown turn into pus and spread to the root, collecting around the root of the tooth. This leads to its infection and gradually invades the adjacent bone and soft tissue. In more severe cases, it can also affect the tonsils, throat, and respiratory passages, causing obstruction and even suffocation.
Occasionally, due to the pressure exerted by wisdom teeth on adjacent teeth, the roots of adjacent teeth undergo resorption. In addition to pain, they also require root canal treatment.
Sometimes, due to the positioning of the wisdom tooth, especially in the upper jaw, dull and vague pain is felt below the ear or in the jaw joint. By examining the condition of the wisdom tooth and removing it, significant help can be provided in controlling these pains.